The article explains how essential oils emerged as potential alternative to antibiotics, in improving gut
health. Due to presence of active ingredients, having wide range of bioactivity, they help in achieving eubiosis and exert beneficial effect on performance of birds.

The demand for poultry products has grown exponentially in last few decades and it is estimated that production will reach up to 130 million tons of chicken meat in 2022, when it will become the most consumed animal meat in the world. Poultry being most efficient feed converters, with a feed conversion ratio in the range of 1.5–1.9. It requires maintenance of high feed efficiency as it plays an essential role in the capacity of the poultry sector to meet the growing demand for poultry products. It comes out as a major challenge, since the intensive production of birds is very prone to be affected by outbreaks of infectious diseases, particularly when unfavourable condition arises.
Optimum gut development is crucial
Gut development starts in embryonic stage. In birds, maximum gut development happens between day 17 of incubation till final hatching. Maturation of gut starts after hatching when chick switches over from yolk nutrition to external feed. At this time, enzymes get secreted and immune system starts to mature as well. The sterile gut gets colonized by an abundant and diverse community of bacteria, influencing the health of birds through their effects on gut morphology, nutrition, pathogenesis and immune responses. At around 21 days, the microbial population in the small intestine is largely established. Since, all environmental microorganisms, including commensals and pathogens would have equivalent freedoms to colonize the gut during this timeframe, it’s notable to keep up eubiosis inside sterile gut.
Healthy Poultry Gut: A Holistic approach
The structure and functioning of the gut are crucial for the health of the poultry. The process of maturation of the gut microbiota throughout the growth cycle of the birds has a resolute impact on the development of the intestinal epithelium and the modulation of the physiological functions required to maintain intestinal homeostasis. To achieve healthy gut, it should have optimum development, balanced microbiome, free from toxins and adequate secretory function. Any alteration or abnormality in these functions leads to gut upset and loss of nutrients.
Feed additives for achieving healthy gut
In recent decades, feed additives gained huge popularity in poultry nutrition to stimulate production performance and to improve welfare and health, especially in stressful periods of life. Many feed additives have a direct or indirect effect on improving the integrity of the intestinal epithelium and on the amount of fermentable substrate available for the intestinal microflora. But, they should be properly selected and administered wisely, as many may have negative impact on gut balance. Feeding of antibiotics as feed additives have often been attributed to dysbiosis & antibiotic resistance, therefore need for natural alternatives came into highlight.
Natural alternatives over Antibiotics

The main advantage of natural alternatives over antibiotics is that they do not usually bear any risk regarding bacterial resistance or undesired residues in products such as meat & eggs. Addition of NGPs to feeds of poultry may have a number of beneficial effects, including:
- Rapid development of a healthy gut microflora
- Stabilization of digestion
- Increased growth performance
- Stimulation and rapid maturation of the immune system
- Reduced incidence of diarrhea
- Improved feed efficiency
- Lower mortality rates
- Higher profitability
Essential oils: A potential natural alternative
Essential oils have a great potential and are generally considered natural, less toxic, and free from harmful residues. They are natural, volatile and aromatic components isolated from plant sources (leaves, fruits, flowers, buds, herbs, seeds, twigs, bark and roots) that have the potential to combat many infectious pathogens.
Essential oils are significantly used as antiseptic, antibacterial, antiviral, anti-parasitic, antifungal, and insecticidal. Hence, essential oils can serve as a powerful tool to reduce the bacterial resistance. In addition to this, they possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-toxigenic, antiquorum-sensing and immune-regulating properties.
Synergistic effects of essential oils potentiate eubiosis
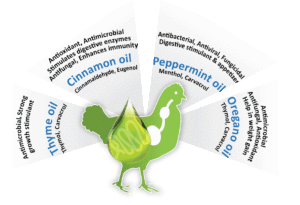
Essential oil shows a potential to improve gut health due to presence of various active ingredients like thymol, carvacrol, eugenol and apparently no side effects. Thymol and Eugenol alter the membrane permeability of pathogens, causing leakage of intracellular contents. In addition, thymol, carvacrol and eugenol exert synergistic or additive antimicrobial effects when supplemented together, even at lower concentration. They show potent activity towards different pathogenic bacteria like Escherichia coli, C. perfringens and Salmonella strains and weak activity towards beneficial Lactobacillus strains, promoting eubiosis in gut of poultry.
Due to their antibacterial activity, they might be able to modify the composition of intestinal microflora and to exert beneficial effects on performance of birds. It also increases digestive enzyme production. Essential oil like Peppermint relaxes the smooth muscle cells that lines the gut.
Table: Essential oils having antibacterial effect on different bacteria
|
Essential oils |
Targeted Bacteria |
| Thyme oil | Clostridium perfringens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, E. coli, Salmonella |
| Cinnamon oil | Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella, E. coli, Bacteroides fragilis |
| Oregano oil | E. coli, Salmonella, Staphylococcus |
| Peppermint oil | E. coli, Listeria, Salmonella, Staphylococcus aureus |
Essential oil showed an overall modification of the microflora, a reduction of Clostridium perfringens, a decrease in E. coli numbers in intestine of poultry birds. Carvacrol and thymol can sensitize the cell walls (including membranes) and cause significant membrane damages, leading to integrity collapse of the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane, leakage of vital intracellular contents and eventually death of the bacterial cells and these has very less effect on useful microbiota.
More details can be reached at www.nutricare.in