Synopsis: This article discusses about importance of overall gut health and working on all contributing factors needful for this approach, considering the complex interactions between different parts i.e., Feed, microbiota and host immunity”
 Gut health is crucial for the performance, health and welfare of poultry. It is important to maximize our profits and minimize loses. It is important for:
Gut health is crucial for the performance, health and welfare of poultry. It is important to maximize our profits and minimize loses. It is important for:
- Utilization of the feed efficiently and at optimum level
- Exploiting the genetic worth of birds so that to have maximum production in the form of meat and eggs
- Achieving the optimal Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR)
- Ensuring quality produce in the form of meat and eggs
- Eliminating digestive problems and gut disturbances
- General health and welfare of the poultry
- Avoiding the spread of pathogenic microorganisms present in feces to other birds in the same batch or the following batches of birds
To have healthy gut, it should have optimum development, balanced microbiome, free from toxins and adequate secretory function. Any alteration or abnormality in these functions leads to gut upset and loss of nutrients.
GIT: An organ with complex functions
GIT is simply described as “the gut” is made up of:
- The epithelium
- Diverse and robust immune system
- Commensal bacteria
Competitive Exclusion: Potent defense mechanism
The presence of normal bacterial microbiota in the intestine makes it more difficult for pathogenic bacteria to enter the animal through the GI tract as there is competition for living space, epithelial attachment sites and available nutrients.
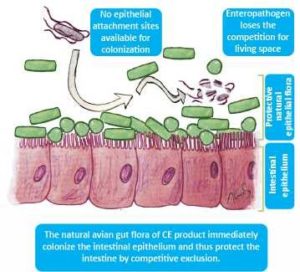 Further, many intestinal microbes are capable of producing antibacterial substances like bacteriocin and the intestinal microbiota is also thought to play a role in the normal development of intestinal immunity. This mechanism, where a healthy intestinal microbiota facilitates the health of the host, is called Competitive Exclusion.
Further, many intestinal microbes are capable of producing antibacterial substances like bacteriocin and the intestinal microbiota is also thought to play a role in the normal development of intestinal immunity. This mechanism, where a healthy intestinal microbiota facilitates the health of the host, is called Competitive Exclusion.
While vaccines may offer effective protection against the bacterial strains they are intended for, a healthy complex intestinal microbiota can reasonably be expected to be beneficial for the health of the bird in a wider perspective, as the whole concept of competitive exclusion has a more universal nature.
Now-a-days, Competitive exclusion products for poultry are most frequently used to establish a natural-like microbiota in the intestine of day-old chicks.
How to get balanced microbiome??
Microbiome comprises of bacteria, fungi, protozoa & viruses. GIT harbours over 640 different species of bacteria & more than 20 different hormones. A balanced microbiome means that the concentration of favourable microbes is more and adequate than unfavourable microbes.
Importance of balanced intestinal microbiota in gut
 With modernization in poultry sector, young chicks are becoming more and more sensitive to bacterial pathogens such as Salmonella sp. In natural habitat, the mother hen acts as the source of the intestinal microbiota of a day-old chick, but young chicks are becoming more susceptible to intestinal disturbances and to several pathogenic infection, due to this missing link.
With modernization in poultry sector, young chicks are becoming more and more sensitive to bacterial pathogens such as Salmonella sp. In natural habitat, the mother hen acts as the source of the intestinal microbiota of a day-old chick, but young chicks are becoming more susceptible to intestinal disturbances and to several pathogenic infection, due to this missing link.
Moving towards alternatives
In past decades, various antibiotics were quite commonly used in intensive poultry production, both to facilitate growth and to avoid problems with bacterial pathogens. However, it is reasonable to assume that many of the antibiotics used also had a negative impact on the natural intestinal and even on environmental microbiota of the poultry flocks. Consumers in many major markets are increasingly aware of the quality aspects of poultry production, not least when it comes to microbiological quality, the use of antibiotics, and animal welfare.
Intensive amount of research has been focused on the development of alternatives to antibiotics to maintain health and performance. Efficacy of alternatives of Antibiotic Growth Promoter (AGP’s) is primarily based on antimicrobial effects and their ability to influence and partly modify the composition and overall concentration of intestinal microflora. Some are Organic acids, Probiotics, Prebiotics, Essential oil compounds, Zn and Cu compounds and have been described by the general term ‘eubiotics’, referring to an optimal balance of microflora in the gastrointestinal tract. Since, a healthy gut is essential for productivity as with a healthy gut, we can work preventively to reduce antibiotic use without losing profits.
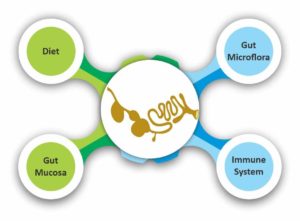
A holistic approach to gut health looks at the whole picture, not just focusing on enteric diseases, but working on all contributing factors and considering the complex interactions between different parts: Feed, microbiota and host immunity.
Salient role of dietary factors in conserving gut integrity
The nature and type of feed ingredients plays paramount role on the integrity of the GIT of birds. Because dietary intake or nutritional status as well as nutrient requirements may be altered as a result of disease or stress, this may eventually alter the gut microflora and intestinal mucosal integrity, resulting in a compromised barrier of the intestinal epithelium. The weakening of the intestinal integrity could result in an increase in bacterial adherence to the mucosa, bacterial translocation, susceptibility to opportunistic bacterial infection, and mis-appropriation of nutrients.
Supplementation of quality feed ingredients helps in maintaining natural gut health. Nutritional deficiency due to imbalance in ration formulation, grain engorgement, microbial load in feed etc. affect gut health.
- Processing feed like extrusion and Pelleting is highly effective in reducing microbial contamination in feedstuffs and in Salmonella control. Pelleting provides scope for utilization of high fibre feed resources. Use of steam- pelleted feed seems to be of value in maintaining gut health.
- Feed toxins and toxicants can also affect the gut integrity; thus, toxin binders are used through feed to bind or adsorb deleterious substances such as mold and fungi-borne mycotoxins.
- Acidifiers or Organic acids play a role in maintaining gut integrity in the way that they reduce the colonization of pathogens (like Salmonella and E. coli) in intestinal wall by lowering the intestinal pH below 6.0, and promoting the normal microflora growth. This environment also increases the efficiency of all digestive enzymes. Daily application of short chain fatty acids such as Butyric acids increases epithelial cell proliferation, quick repairing of the intestine, increased villous height and in turn increased absorptive capacity.
- Additional supplementation of enzymes can enhance digestive capacity of birds. Feeding high viscosity cereal grains to broilers result in larger microbial populations in the ileum. Viscous environment slows down digestion processes, and encapsulates nutrients, making them inaccessible to digestive enzymes. Viscous gels are formed in the digesta by the soluble NSP, which are not digested by the animal’s own enzymes, thus inhibit absorption. The addition of enzymes to address NSP viscosity can improve gut health, feed efficiency, improve manure quality and facilitate the use of lower cost feed ingredients.
GIT microbiota
The rich bacterial community that makes up the gut micro flora play an important role for the host through changes in the morphology of gut, nutrition, pathogenesis of enteric diseases, immune response and alterations in colonization resistance. The shift in composition of this microflora results in production and efficiency losses often in the absence of any clinical signs. Useful microbes (commensal bacteria) in gut play a positive role in controlling the gut flora and stimulate the development of the gut wall. Hence, microbial balance of gut is utmost important in maintaining gut integrity.
- Probiotics are live microbial feed supplements which beneficially affect the host by improving its intestinal microbial balance. These are most effective in birds during microflora development or when microflora stability is impaired. Benefit of probiotics with respect to health status and performance is expected to be highest in chicks as they have not yet developed a stable gut microflora. Competitive adhesion of probiotic microorganisms to epithelial receptors prevents the attachment of pathogenic bacteria. Besides this, they increase synthesis of lactic acid to maintain intestinal pH, increases production of specific antibacterial substances, reduces production of toxic amines and decrease ammonia level in the gastro-intestinal tract.
- Prebiotics are non-digestible oligosaccharides which are fed in order to control or manipulate microbial composition and activity, thereby assisting to maintain a beneficial microflora. Prebiotics include a diversity of non-starch polysaccharides (NSP) or oligosaccharides including mannan-oligosaccharide (MOS), fructans (FOS and inulin), oligofructose etc. Dietary inclusion levels of potential prebiotics are usually 0.1 to 0.5 per cent. They give resistance to gastric acidity, helps hydrolysis by digestive enzymes and enhances gastrointestinal absorption, fermentation by intestinal microflora and selective stimulation of the growth and/or activity of those intestinal bacteria that contribute to health and well-being.
- Synbiotics are the combination of prebiotics and probiotics. Although use of probiotic formulations may well help in achieving these benefits, it is also possible to increase and maintain a healthy bacterial gut flora by increasing the amounts of prebiotics in the diet such as inulin (naturally occurring oligosaccharides), raw oats, and unrefined wheat. As probiotics are mainly active in the small intestine and prebiotics are only effective in the large intestine, the combination of the two gives a synergistic effect. Appropriate combinations of pre- and probiotics are termed as synbiotics.
- Essential oils show a potential for the replacement of antibiotic growth promoters due to presence of various active ingredients like thymol, carvacrol, eugenol and apparently no side effects. Due to their antibacterial activity, they might be able to modify the composition of intestinal microflora and to exert beneficial effects on performance of broilers and layers. It also increases digestive enzyme production. Essential oil showed an overall modification of the microflora, a reduction of Clostridium perfringens, a decrease in E. coli numbers in intestine of birds. Cinnamaldehyde has shown to inhibit the growth of Clostridium perfringens and Bacteroides fragilis. Carvacrol and thymol can sensitize the cell walls (including membranes) and cause significant membrane damages, leading to integrity collapse of the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane, leakage of vital intracellular contents and eventually death of the bacterial cells and these has very less effect on useful microbiota.
Stronger the gut immunity, Better the health
The intestinal immune system includes:
- Mucosal layer
- Tightly interconnected intestinal epithelial cells
- Soluble immunoglobulin A
- Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs)
Gut immune responses are tightly controlled to remain tolerant of the commensal microbiota, while concurrently maintaining the capacity to respond appropriately to harmful insults.
Maintaining gut immune homeostasis, while mounting protective immunity to pathogens is primarily achieved through:
(1) Limiting direct bacterial contact with the intestinal epithelium
(2) Rapid detection and removal of pathogens that penetrate the epithelium.
The gut microbiota derives nutrients from the host’s diet or endogenous secretions, whilst enhancing the nutritional value of the diet through the synthesis of essential nutrients (e.g., vitamins) and the production of complimentary enzymes (e.g., non-starch polysaccharidases). During the depolymerization of dietary polysaccharides, gut bacteria produce short chain fatty acids (acetate followed by propionate and butyrate).
- Probiotics colonizes the intestine with microbes with desirable attributes that can promote competitive exclusion and/or promote beneficial gut barrier and immune function.
- Prebiotics helps in shaping the gut microbiome and, in turn, immune capability.
- Exogenous enzymes, plant-derived compounds, organic acids including butyric acid and mycotoxin mitigation (limit intestinal damage and suppression of immune responses) for strengthening gut immunity.
Combinations of probiotics, prebiotics and essential oil can be adopted in order to get all the benefits at once, to achieve holistic health. Nutricare offers a combination of probiotics, prebiotics and essential oil fortified with vitamins and minerals, which is effective alternative to antibiotics. Power of oregano oil, thyme oil, cinnamaldehyde, prebiotics, probiotics and nutrients effectively reduce pathogens like E. coli, Salmonella, Clostridia and increases the gut fauna like Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Saccharomyces. By enhancing intestinal villi length, increases nutrient absorption, thus maximises weight gain and improves the carcass characteristics. It also aids in enhancing digestive secretions and digestibility of feed. Boost’s immunity, stimulates growth and has antioxidant role.
More details can be reached at www.nutricare.in
Previous article by the Author(s): Destressing Using Natural Approach